Spyglass
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Spyglass [1] is an Apple app that implements a compass. It uses your camera, maps (internet), location and calculates height, direction, speed and GPS position.
Definitions
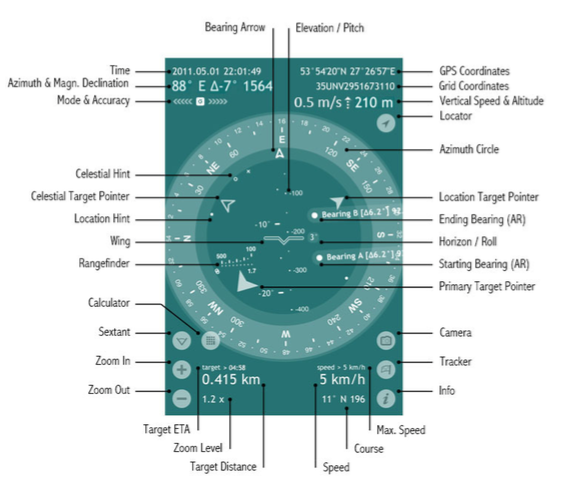
- Elevation/Pitch angle is the angle between the horizontal line that your sight forms when you look straight and the line to some particular point above.
In Spyglass the elevation angle is marked with Wing or Crosshair and shows how much your device is tilted back or forth. The elevation scale is calibrated with degrees and mils and is perpendicular to the horizon line. - GPS Coordinates – geodesic latitude and longitude coordinates of your current location, expressed in degrees, minutes and seconds (depending on the chosen coordinate format) along with the corresponding hemispheres.
- Grid Coordinates – your current location in the coordinates of the chosen grid coordinate system (MGRS, UTM or OSGB/BNG), to which numbers and letters are assigned for use in designating a point on a gridded map.
- Vertical Speed indicator shows your current vertical speed in knots, feet per minute or metres per second, depending on your country and set-up units.
The vertical speed data will appear to the left of the altitude readings for vertical speeds higher than 80fpm (0.4m/s). - Altitude – current height above sea level.
- Locator lets you return to the actual GPS readings after manual settings.
- Azimuth Circle measures azimuths and bearings. In Spyglass the azimuth circle is graduated with degrees, mils and points of the compass (marking divisions of the four cardinal directions).
The current azimuth or bearing is marked with the Bearing Arrow. - Location Target Pointer – points in the direction of an important location or object.
- Starting Bearing (AR) and Ending Bearing (AR) are the augmented reality (AR) markers, used for the visual angle measurement, performed by the Sextant tool.
- Horizon/Roll angle shows how much the device is tilted left or right.
- Primary Target Pointer – points in the direction of the target of your primary interest.
- Camera lets you instantly take pictures or screenshots overlaid with all the necessary location data.
- Tracker opens the Destinations menu, via which you can add new destinations (bearings, locations, terrestrial and celestial objects) and manage the saved ones.
- Info opens the Settings & Calibration menu.
- Max. Speed – the maximum movement speed within the current session. Course – your current movement direction.
- Course – your current movement direction.
- Speed – your current movement speed (in kilometers, miles or nautical miles – depending on your settings).
- Target Distance – the distance to the primary target (if it’s a terrestrial object) or the azimuth and elevation of the primary target (if it’s a celestial body).
- Zoom Level – zoom factor for the live camera picture / scale factor for maps.
- Target ETA – estimated time of arrival at your primary target (provided that the distance decreases over time and the current speed is over 1 km/h).
- Zoom In and Zoom Out magnify and minify either the live camera picture or maps – whichever is active.
The corresponding zoom level is also applied to the augmented reality object mapping and the measurement scales of the HUD.
You can also magnify and minify the picture with zoom and pinch gestures. - Sextant/Inclinometer is an instrument for measuring angles of slope (or tilt), elevation or depression of an object with respect to gravity. In Spyglass it measures azimuth (yaw), elevation (pitch), horizon (roll) angle deltas and lets you visually measure angles between two bearings, two points on the live camera image or two device attitudes.
- Calculator button appears to the right of the Sextant button after the Starting and Ending Bearings have been set.
Angular Calculator allows to calculate distances to objects, angles between objects and sizes of objects. - Rangefinder reticle allows you to quickly measure the distance to objects of a determinate height (1.7m/5.6ft).
- Wing reticle represents the actual wings in the attitude indicator (an instrument used in an aircraft to inform the pilot of the orientation of the aircraft relative to Earth's horizon) and is used to align the horizon.
It can be turned off or replaced with the Crosshair reticle in the settings.
The reticle also marks the current elevation angle on the Elevation scale. - Location Hint – points in the direction of a secondary location or object.
- Celestial Target Pointer – points in the direction of an important celestial object.
- Celestial Hint – points in the direction of a secondary celestial object.
- Mode & Accuracy – the current compass mode and its accuracy along with the current accuracy of GPS.
- “G” stands for the gyrocompass mode,
- “M” – for manual orientation,
- “C” – for the car mode and
- “∩”– for the magnetic mode.
The arrows pointing to the left show the accuracy level of magnetic compass, while the arrows pointing to the right show the current GPS accuracy.
- Azimuth represents the direction to an object referenced from due north and measured clockwise through a full 360° circle.
In Spyglass the current true or magnetic geodesic azimuth is shown in degrees and mils and is complemented by the corresponding intercardinal directions. - Magnetic Declination is the angle between magnetic north and true north.
- Time – current date (YYYY.MM.DD) and time (HH:MM:SS).
- Bearing Arrow points in the current direction you are facing and marks the correspondent azimuth.
The Elevation/Pitch scale serves here as the shaft of the Bearing Arrow.
Tracking
The tracking button, the litlle flag in the right bottom corner of the HUD, enables:
- Manage destinations
- Add Map locations
- Add Current Bearing
- Add Current Location
- Add with Distance
Add Your Current Location/Bearing
Adding your current location for tracking might be useful when you are leaving your car somewhere in the wilds or in a parking lot and will need to get back to it later.
To add your current location you need to:
|
When you are indoors the GPS readings may be off, so you can add your current location via maps for better precision:
|
To add your current bearing
|
To add a location via maps:
|
To add a location with the distance to it:
|
To add a location with known coordinates:
|
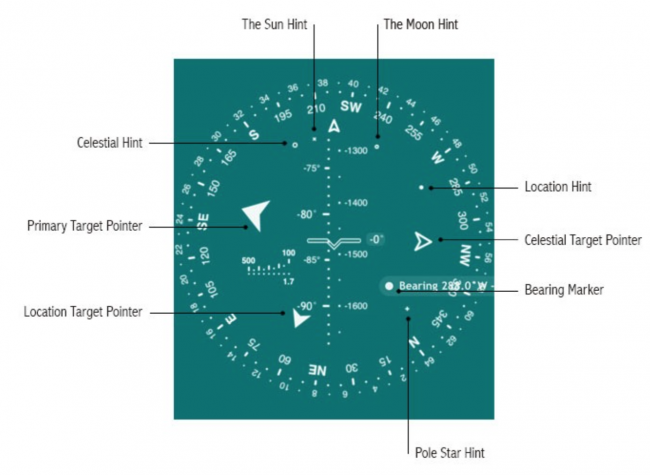
- Primary Target Pointer – magnified arrow that points in the direction of your primary target
- Location Target Pointer (Big pointer) – solid arrow that points in the direction of an important location or terrestrial object
- Celestial Target Pointer (Big pointer) – hollow arrow that points in the direction of an important celestial object
- Location Hint – small solid circle that hints the direction to a location or terrestrial object of secondary importance
- Celestial Hint – small hollow circle that hints the direction to a celestial object of secondary importance
- Bearing Marker – big solid circle that marks a bearing
- The Sun Hint - tiny “x” that hints the direction to the Sun
- The Moon Hint - tiny “o” that hints the direction to the Moon
- Pole Star Hint - tiny “+” that hints the direction to the North Star (Polaris)
See also
Reference
- ↑ Happy Magenta, Spyglass Homepage.