Query Language
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Starting to make some tips and tricks on the SQL Query Language. Assuming the very basic CRUD commands (i.e. Create, Insert, Update, Select and Delete) are known. if not look at one of the following sites:
- Baygon Group, Basic SQL Commands
- W3Schools, SQL Tutorial.
Joins
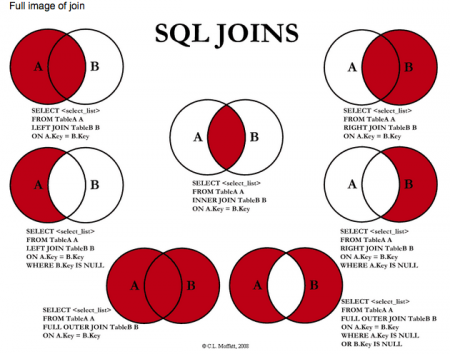
SQL joins are used to combine rows from two or more tables. The most common type of join is: SQL INNER JOIN (simple join). An SQL INNER JOIN return all rows from multiple tables where the join condition is met.
Example is the following 2 tables:
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The SQL command:
SELECT Orders.OrderID, Customers.CustomerName, Orders.OrderDate FROM Orders INNER JOIN Customers ON Orders.CustomerID = Customers.CustomerID;
| Result set | ||
|---|---|---|
| OrderID | CustomerName | OrderDate |
| 10308 | Ana Trujillo Emparedados y helados | 9/18/1996 |
| 10365 | Antonio Moreno Taquería | 11/27/1996 |
| 10383 | Around the Horn | 12/16/1996 |
| 10355 | Around the Horn | 11/15/1996 |
| 10278 | Berglunds snabbköp | 8/12/1996 |
Other possible join are:
- INNER JOIN or JOIN: Returns all rows when there is at least one match in both tables.
- LEFT JOIN: Return all rows from the left table, and the matched rows from the right table.
- RIGHT JOIN: Return all rows from the right table, and the matched rows from the left table
- FULL JOIN: Return all rows when there is a match in one of the tables.
Inner Join or Join
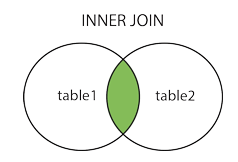
Alias:
- join
- inner join
Syntax:
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1 INNER JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
See:
- W3Schools Inner Join.
Left Join
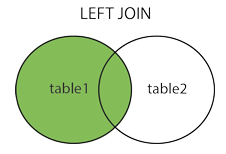
Alias:
- Left join
- Left outer join
Syntax:
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1 LEFT JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
See:
- W3Schools, Left outer join
Right Join
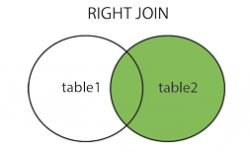
Alias:
- Right join
- Right outer join
Syntax:
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1 RIGHT JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
See:
- W3Schools, Right outer join
Full Outer Join
Alias:
- Full outer join
Syntax:
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1 FULL OUTER JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
See:
- W3Schools, Full outer join
Union
The SQL UNION operator combines the result of two or more SELECT statements.
There are 2 different Union commands:
- union, which selects all different unique entries.
- union all, selects all unique entries.
NB: Notice that
- Each SELECT statement within the UNION must have the same number of columns.
- Columns must also have similar data types.
- Columns in each SELECT statement must be in the same order.
See:
- W3School, Union examples and Union All examples.
See also
- W3School, SQL Quick Reference