Whois: Difference between revisions
m →CIDR |
|||
| Line 486: | Line 486: | ||
* [https://www.ipaddressguide.com/cidr ipaddressguide.com], CIDR transform CIDR to Physical IP-Addresses. | * [https://www.ipaddressguide.com/cidr ipaddressguide.com], CIDR transform CIDR to Physical IP-Addresses. | ||
* [https://www.harmfrielink.nl/Utility harmfrielink utility], Tools, CIDR to range. | |||
== Web Crawlers == | == Web Crawlers == | ||
Revision as of 13:40, 30 July 2023
Whois (pronounced as the phrase who is) is a query and response protocol that is widely used for querying databases that store the registered users or assignees of an Internet resource, such as a domain name, an IP address block, or an autonomous system, but is also used for a wider range of other information [1].
Implementation
Whois is first implemented on UNIX and is available for all operation systems. The implementation may vary in functionality.
Servers
| <img title="Regional Internet Registries" width="400" src=http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/9/95/Regional_Internet_Registries_world_map.svg /> | Whois servers operated by Regional Internet Registries (RIR) can be queried directly to determine the Internet Service Provider responsible for a particular resource: [2]
|
Services
Is it possible to get Whois information for free? Yes and no.
- Yes for doing lookups using the unix whois clients using port 43.
- Yes for doing queries using the RESTful method/interfaces of the providers (if defined, see below).
- No for bulk lookups. The services are limited by the number of queries. The first 100-500 queries are for free. The next have to be paid. Example
Also the given information differs in quality. See the examples below.
If you host your website on an external server, the owner may have closed port 43 for whois access. In that case you'll need an http-lookup without using port 43. A very popular and good service is provided by http://www.woisxmlapi.com. Unfortunately not for free.
Afrinic
Whois CLI
The Africa Network Information Centre (AfriNIC) command-line whois: <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> $ whois -h whois.afrinic.net 89.237.134.1 </syntaxhighlight>
RESTful
The RESTful Interface is available through RIPE using:
- http://rest.db.ripe.net/search.xml?query-string=<ip-address>&source=afrinic-grs
An example :
Will give you an address in Kenya.
ARIN
Whois CLI
American Registry for Internet Number (ARIN) command-line whois: <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> $ whois -h whois.arin.net 66.249.75.160 </syntaxhighlight>
RESTful
# # Query terms are ambiguous. The query is assumed to be: # "n 66.249.75.160" # # Use "?" to get help. # # # The following results may also be obtained via: # http://whois.arin.net/rest/nets;q=66.249.75.160?showDetails=true&showARIN=false&ext=netref2 # NetRange: 66.249.64.0 - 66.249.95.255 CIDR: 66.249.64.0/19 OriginAS: NetName: GOOGLE NetHandle: NET-66-249-64-0-1 Parent: NET-66-0-0-0-0 NetType: Direct Allocation RegDate: 2004-03-05 Updated: 2012-02-24 Ref: http://whois.arin.net/rest/net/NET-66-249-64-0-1 OrgName: Google Inc. OrgId: GOGL Address: 1600 Amphitheatre Parkway City: Mountain View StateProv: CA PostalCode: 94043 Country: US RegDate: 2000-03-30 Updated: 2011-09-24 Ref: http://whois.arin.net/rest/org/GOGL OrgAbuseHandle: ZG39-ARIN OrgAbuseName: Google Inc OrgAbusePhone: +1-650-253-0000 OrgAbuseEmail: arin-contact@google.com OrgAbuseRef: http://whois.arin.net/rest/poc/ZG39-ARIN OrgTechHandle: ZG39-ARIN OrgTechName: Google Inc OrgTechPhone: +1-650-253-0000 OrgTechEmail: arin-contact@google.com OrgTechRef: http://whois.arin.net/rest/poc/ZG39-ARIN # # ARIN WHOIS data and services are subject to the Terms of Use # available at: https://www.arin.net/whois_tou.html #
The RESTful interface is available though:
- http://whois.arin.net/rest/nets;q=<ip>?showDetails=true
- https://rest.db.ripe.net/search.xml?query-string=<ip-address>&source=arin-grs
- Example: 'https://rest.db.ripe.net/search.xml?query-string=17.58.100.215&source=arin-grs' is an Apple owned IP-Address.
APNIC
Whois CLI
Asia-Pacific Network Information Centre (APNIC) command-line interface: <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> $ whois -h whois.apnic.net 66.249.75.160 </syntaxhighlight>
% [whois.apnic.net node-7] % Whois data copyright terms http://www.apnic.net/db/dbcopyright.html inetnum: 66.0.0.0 - 66.255.255.255 netname: ARIN-CIDR-BLOCK descr: Not allocated by APNIC remarks: ------------------------------------------------------ remarks: remarks: Important: remarks: remarks: Details of networks in this range are not registered remarks: in the APNIC Whois Database. remarks: remarks: Please search the ARIN Whois, which contains remarks: details of IP addresses allocated in North America, remarks: parts of the Caribbean, and sub-equatorial Africa: remarks: remarks: website: https://ws.arin.net/whois remarks: command line: whois.arin.net remarks: remarks: ------------------------------------------------------ country: AU admin-c: IANA1-AP tech-c: IANA1-AP mnt-by: MAINT-APNIC-AP mnt-lower: MAINT-APNIC-AP status: ALLOCATED PORTABLE changed: hm-changed@apnic.net 20030403 changed: hm-changed@apnic.net 20040926 changed: hm-changed@apnic.net 20090501 source: APNIC role: Internet Assigned Numbers Authority address: see http://www.iana.org. country: US phone: +1-310-823-9358 e-mail: nobody@apnic.net admin-c: IANA1-AP tech-c: IANA1-AP nic-hdl: IANA1-AP remarks: For more information on IANA services remarks: go to IANA web site at http://www.iana.org. mnt-by: MAINT-APNIC-AP changed: helpdesk@apnic.net 20110811 changed: hm-changed@apnic.net 20111206 source: APNIC
RESTful
The RESTful interface:
- http://apps.db.ripe.net/whois/search?source=apnic&query-string=%s&flags=%s
- https://rest.db.ripe.net/search.xml?query-string=<ip-address>&source=apnic-grs
Ripe
Whois CLI
$ whois -h whois.ripe.net 66.249.75.160 % This is the RIPE Database query service. % The objects are in RPSL format. % % The RIPE Database is subject to Terms and Conditions. % See http://www.ripe.net/db/support/db-terms-conditions.pdf % Note: this output has been filtered. % To receive output for a database update, use the "-B" flag. % Information related to '0.0.0.0 - 255.255.255.255' inetnum: 0.0.0.0 - 255.255.255.255 netname: IANA-BLK descr: The whole IPv4 address space country: EU # Country field is actually all countries in the world and not just EU countries org: ORG-IANA1-RIPE admin-c: IANA1-RIPE tech-c: IANA1-RIPE status: ALLOCATED UNSPECIFIED remarks: This object represents all IPv4 addresses. remarks: If you see this object as a result of a single IP query, it remarks: means that the IP address you are querying is not managed by remarks: the RIPE NCC but by one of the other five RIRs. It might remarks: also be an address that has been reserved by the IETF as part remarks: of a protocol or test range. remarks: You can find the whois server to query, or the remarks: IANA registry to query on this web page: remarks: http://www.iana.org/assignments/ipv4-address-space/ipv4-address-space.xml mnt-by: RIPE-NCC-HM-MNT mnt-lower: RIPE-NCC-HM-MNT mnt-routes: RIPE-NCC-RPSL-MNT source: RIPE # Filtered organisation: ORG-IANA1-RIPE org-name: Internet Assigned Numbers Authority org-type: IANA address: see http://www.iana.org remarks: The IANA allocates IP addresses and AS number blocks to RIRs remarks: see http://www.iana.org/ipaddress/ip-addresses.htm remarks: and http://www.iana.org/assignments/as-numbers admin-c: IANA1-RIPE tech-c: IANA1-RIPE mnt-ref: RIPE-NCC-HM-MNT mnt-by: RIPE-NCC-HM-MNT source: RIPE # Filtered role: Internet Assigned Numbers Authority address: see http://www.iana.org. admin-c: IANA1-RIPE tech-c: IANA1-RIPE nic-hdl: IANA1-RIPE remarks: For more information on IANA services remarks: go to IANA web site at http://www.iana.org. mnt-by: RIPE-NCC-MNT source: RIPE # Filtered % This query was served by the RIPE Database Query Service version 1.42 (WHOIS4)
RESTful
The RESTfull interface
- https://rest.db.ripe.net/search.xml?query-string=<ip-address>&source=ripe-grs
LACNIC
There is a RESTful interface:
- LACNIC doc-pdf, RESTful description.
- http://restwhois.labs.lacnic.net/restfulwhois/ip/<ip>
or
$ whois -h whois.lacnic.net 181.231.166.73 % IP Client: xx.xxx.xxx.xxx % LACNIC resource: whois.lacnic.net % Copyright LACNIC lacnic.net % The data below is provided for information purposes % and to assist persons in obtaining information about or % related to AS and IP numbers registrations % By submitting a whois query, you agree to use this data % only for lawful purposes. % 2023-07-30 08:20:10 (-03 -03:00) inetnum: 181.230.0.0/15 status: allocated aut-num: AS7303 owner: Telecom Argentina S.A. ownerid: AR-TAST-LACNIC responsible: Administrador IP address: Dorrego, 2520, Piso 11 address: 1425 - Buenos Aires - country: AR phone: +54 1149684975 [0000] owner-c: ADI2 tech-c: ADI2 abuse-c: ADI2 inetrev: 181.230.0.0/15 nserver: O200.PRIMA.COM.AR nsstat: 20230726 AA nslastaa: 20230726 nserver: O2000.PRIMA.COM.AR nsstat: 20230726 AA nslastaa: 20230726 created: 20131030 changed: 20180529 nic-hdl: ADI2 person: Administrador IP e-mail: abuse@teco.com.ar address: Dorrego, 2502, piso 11 address: 1425 - Buenos Aires - country: AR phone: +54 11 4968 [4975] created: 20020909 changed: 20211227
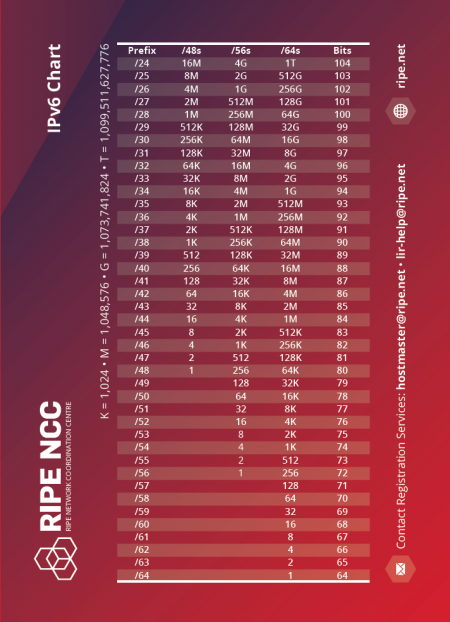
IPv6 Addresses
The rapid grow of the Internet world wide has created a problem for the IPv4 IP-Addresses, the possible number of IP-Addresses has been reached.
Meaning there have to come a solution a larger number of unique IP-addresses the IPv6.
IPv6 addresses are classified by the primary addressing and routing methodologies common in networking: [3]
- A unicast address identifies a single network interface.
The Internet Protocol delivers packets sent to a unicast address to that specific interface. - An anycast address is assigned to a group of interfaces, usually belonging to different nodes.
A packet sent to an anycast address is delivered to just one of the member interfaces, typically the nearest host, according to the routing protocol's definition of distance. Anycast addresses cannot be identified easily, they have the same format as unicast addresses, and differ only by their presence in the network at multiple points. Almost any unicast address can be employed as an anycast address. - A multicast address is also used by multiple hosts, which acquire the multicast address destination by participating in the multicast distribution protocol among the network routers.
A packet that is sent to a multicast address is delivered to all interfaces that have joined the corresponding multicast group.
IPv6 does not implement broadcast addressing. Broadcast's traditional role is subsumed by multicast addressing to the all-nodes link-local multicast group ff02::1. However, the use of the all-nodes group is not recommended, and most IPv6 protocols use a dedicated link-local multicast group to avoid disturbing every interface in the network.
An IPv6 address consists of 128 bits.
For each of the major addressing and routing methodologies, various address formats are recognized by logically dividing the 128 address bits into bit groups and establishing rules for associating the values of these bit groups with special addressing features.
Unicast and anycast address format
Unicast and anycast addresses are typically composed of two logical parts:
- a 64-bit network prefix used for routing,
- and a 64-bit interface identifier used to identify a host's network interface.
General unicast address format (routing prefix size varies) bits 48 (or more) 16 (or fewer) 64 field routing prefix subnet id interface identifier
The network prefix (the routing prefix combined with the subnet id) is contained in the most significant 64 bits of the address. The size of the routing prefix may vary; a larger prefix size means a smaller subnet id size. The bits of the subnet id(entifier) field are available to the network administrator to define subnets within the given network. The 64-bit interface identifier is either automatically generated from the interface's MAC Address using the modified EUI-64 format, obtained from a DHCPv6 server, automatically established randomly, or assigned manually.
A link-local address is also based on the interface identifier, but uses a different format for the network prefix.
Link-local address format bits 10 54 64 field prefix zeroes interface identifier
The prefix field contains the binary value 1111111010. The 54 zeroes that follow make the total network prefix the same for all link-local addresses (Template:IPaddr link-local address prefix), rendering them non-routable.
Multicast address format
Multicast addresses are formed according to several specific formatting rules, depending on the application.
General multicast address format bits 8 4 4 112 field prefix flg sc group ID
The prefix holds the binary value 11111111 for any multicast address.
Currently, 3 of the 4 flag bits in the flg field are defined; the most-significant flag bit is reserved for future use.
Multicast address flags[4] bit flag Meaning when 0 Meaning when 1 8 reserved reserved reserved 9 R (Rendezvous) Rendezvous point not embedded Rendezvous point embedded 10 P (Prefix) Without prefix information Address based on network prefix 11 T (Transient) Well-known multicast address Dynamically assigned multicast address
The 4-bit scope field (sc) is used to indicate where the address is valid and unique.
There are special multicast addresses, like Solicited Node.
Solicited-Node multicast address format bits 8 4 4 79 9 24 field prefix flg sc zeroes ones unicast address
The sc(ope) field holds the binary value 0010 (link-local). Solicited-node multicast addresses are computed as a function of a node's unicast or anycast addresses. A solicited-node multicast address is created by copying the last 24 bits of a unicast or anycast address to the last 24 bits of the multicast address.
Unicast-prefix-based multicast address format bits 8 4 4 4 4 8 64 32 field prefix flg sc res riid plen network prefix group ID
Link-scoped multicast addresses use a comparable format.
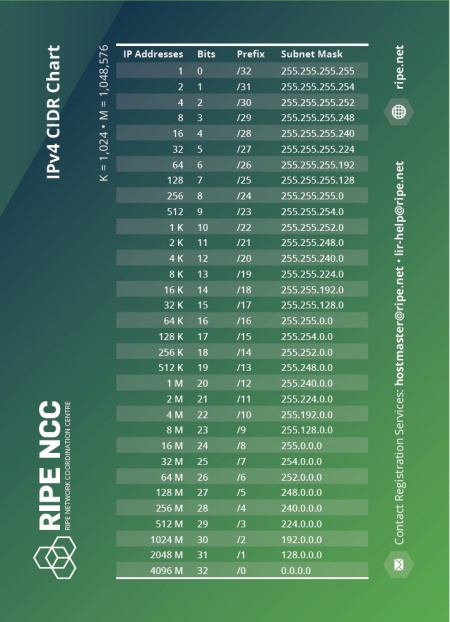
CIDR
A detailed view in CIDR [5]
- ipaddressguide.com, CIDR transform CIDR to Physical IP-Addresses.
- harmfrielink utility, Tools, CIDR to range.
Web Crawlers
Website Crawler, the hard-working, lesser-known, essential component of a search engine.
A web crawler is a bot—a software program—that systematically visits a website, or sites, and catalogs the data it finds.
It’s a figurative bug that methodically locates, chews on, digests, and stores digital content to help create a searchable index.
| IP-Range | NetName | Location | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 17.0.0.0 - 17.255.255.255 | Apple | Cupertino | https://rdap.arin.net/registry/entity/APPLEC-1-Z |
| 85.25.176.0 - 85.25.179.255 | BSB Service | Berlin | - |
| 66.249.64.0 - 66.249.95.255 | Mountain View | https://rdap.arin.net/registry/entity/GOGL | |
| 207.46.0.0 - 207.46.255.255 | Microsoft | Redmond (Quincy) | https://rdap.arin.net/registry/entity/MSFT |
| 93.158.161.0 - 93.158.161.255 | Yandex LLC | Moscow | - |
See also
- Ripe.net, Whois reference Card
Alternatives
- IpDb.at, Covers all different Whois lookups, not so accurate on the location. Nearly the same information as 'lookup.net' and 'MyIp'.
- Lookip.net, Covers all different Whois lookups, easy to use and is also accurate on the location of the real IP-owner.
- MyIp, Covers all different Whois lookups, easy to use, but the location is not very accurate.
Reference
- ↑ Whois, The definition is taken form wikipedia.
- ↑ math utah edu, Whois Servers on the world. Including a list of domain names.
- ↑ IPv6 Addresses, Wikipedia on IPv6.
- ↑ IPv6 Essentials, Author: Silvia Hagen, Publisher: O'Reilly, Edition: Second, Date: May 2006, isbn: 978-0-596-10058-2
- ↑ Ripe.net, Understanding IP-Addressing.