Apple OSX: Difference between revisions
m →Email |
|||
| Line 131: | Line 131: | ||
== Email Sync Multiple Devices == | == Email Sync Multiple Devices == | ||
If you are using the same email account on multiple devices, the send-emails are only stored on the device that has sent the email. | If you are using the same email account on multiple devices, the send-emails are only stored on the device that has sent the email <ref>[https://www.lifewire.com/automatically-bcc-os-x-mail-1172861 LifeWire] Automatically bcc osx mail</ref>. | ||
<br>That's not always what you want. Suppose: | <br>That's not always what you want. Suppose: | ||
* Send email to someone from your macbook-pro and you can not find the sent mail on your iMac which has the full-copy of the mailbox. | * Send email to someone from your macbook-pro and you can not find the sent mail on your iMac which has the full-copy of the mailbox. | ||
Revision as of 13:15, 11 August 2018
The goal of this page is to give information on OSX and related issues.
Is that necessary? Yes, because Apple products have a lot of hidden features!
Apple/Unicode Characters
How to get the correct Apple tokens/sign/characters for typical computer operations.
For more tokens and their character representation look at HarmFrielink Unicode characters.
There are also links to more sites with characters and their representation.
|
|
|
Disk Access
Apple OSX can read form a lot of disk-formats, but can not write to them. First problem, windows NTFS.
Tuxera
Mac OS X does not support writing to Microsoft Windows formatted NTFS volumes out-of-the box. The solution is here. Tuxera [1] NTFS for Mac is our commercial read/write NTFS software for Mac users. Tuxera NTFS for Mac delivers the fastest NTFS data transfer speeds you can have on Mac while protecting your data with its new, smart caching layer.
The software fully supports all versions of Mac OS X from 10.4 (Tiger) onwards, including of course Mac OS X 10.8 (Mountain Lion) with its 64-bit kernel, and comes with advanced features only available from Tuxera such as support for NTFS extended attributes. Tuxera NTFS for Mac is compatible with popular virtualization and encryption solutions including Parallels Desktop®, VMware Fusion® and TrueCrypt.
Email Sync Multiple Devices
If you are using the same email account on multiple devices, the send-emails are only stored on the device that has sent the email [2].
That's not always what you want. Suppose:
- Send email to someone from your macbook-pro and you can not find the sent mail on your iMac which has the full-copy of the mailbox.
- The sent mail is stored in the inbox/sentmail of your mailbook-pro.
You can prevent this behaviour by sending a copy of the sent mail using the BCC-option.
And that can be done automatically! How:
Open terminal
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash" line>
- First check if there is already an email-bcc-rule active.
$ defaults read com.apple.mail UserHeaders. 2018-08-11 12:27:58.107 defaults[37344:8567991] The domain/default pair of (/Users/HaFrMpro/Library/Containers/com.apple.mail/Data/Library/Preferences/com.apple.mail, UserHeaders.) does not exist
- Now add the bcc you want to use
$ defaults write com.apple.mail UserHeaders '{"Bcc" = "xxx@harmfrielink.nl"; }' /Sources/GitLab/PHP-Web-Start/src:HaFrMpro$ defaults read com.apple.mail UserHeaders {
Bcc = "xxx@harmfrielink.nl";
} </syntaxhighlight> Optional you can change the mail-signature of the devices so you can find the sending-device of the email.
Email Signature
One of the toughest things to make is a nice signature in Apple Email. The cause comes of the complicated way mail is handling the HTML code insight the mail.
See for more how to do it on : http://mydesignpad.com/create-a-html-email-signature-for-mac-os-x-mountain-lion-10-8/.
An excerpt of all the steps:
- Step 1: Designing the HTML/CSS
- Step 2: Create Placeholder Signature in Mail
- Step 3: Open the Signatures Folder
- Step 4: Update Placeholder Signature
- Step 5: Lock Updated Signature File – Important Step!
- Step 6: Check Installation
Finder
Zichtbaar maken van UNIX systeem mappen. OS X is gebaseerd op UNIX, waardoor het mogelijk is om UNIX programma’s te draaien.
Omdat UNIX het belangrijkste deel van de systeemlaag is zijn er enkele systeembestanden in de Finder onzichtbaar gemaakt om fouten of beschadiging aan het systeem te vermijden.
Maar heb je deze bestanden en mappen een keer nodig dan kan je deze simpelweg activeren doormiddel van een command in de terminal uit te voeren.
Nota Bene: Het zichtbaar maken van deze bestanden zijn geheel op eigen risico bij fouten kan het systeem compleet niet meer werken!
defaults write com.apple.Finder AppleShowAllFiles TRUE
Om de wijzigingen door te voeren dien je de Finder te herstarten, doormiddel van het Apple menu via Forceer Stop of een terminal command:
killall Finder
Hierdoor is het nu mogelik belangrijke systeemmappen zichtbaar te maken en te gebruiken.
Wijzigingen zijn terug te draaien door het omgekeerde TRUE naar FALSE te wijzigingen in de terminal.
defaults write com.apple.Finder AppleShowAllFiles FALSE
Na de wijziging dien je de Finder te herstarten.
killall Finder
Nu zijn alle instellingen weer naar behoren en zal je geen belangrijke systeem mappen meer zien
Search Email Rules
Solution for Apple OSX 10.8.1 (Lion).
The location of the mailbox rules: ~/Library/Mail/V2/MailData/MessageRules.plist
Open the file with your favourite editor and search for the item your looking for.
The name of the rules is defined in the XML-tags:
<key>RuleName</key>
<string>Name-of-the-Rule</string>
Be careful not to make changes in this file directly, cause this may damage your rules!!
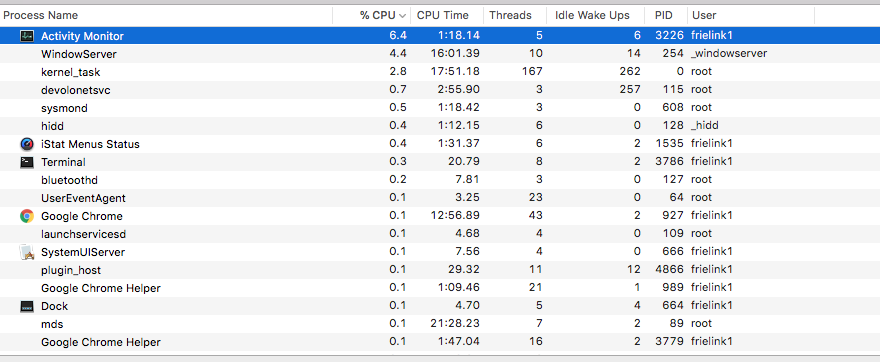
Monitor your Mac
Monitor your Mac gives you a list of powerful and useful terminal UNIX commands to see the health and performance of your OSX device [3].
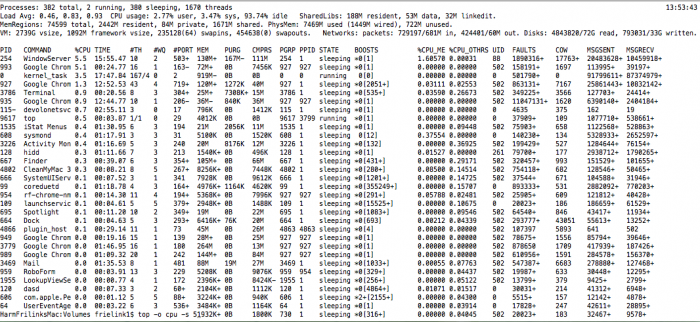
Top
The UNIX command top is an equivalent of the Activity Monitor with some slight differences. <syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
- Opens the top window sorted on CPU and 5 seconds update.
$ top -o cpu -s 5 </syntaxhighlight>
| Top command | OSX Activity Monitor |
|---|---|
 |
|
List open files
The lsof command used in many Linux/Unix like system that is used to display list of all the open files and the processes.
The open files included are disk files, network sockets, pipes, devices and processes.
One of the main reason for using this command is when a disk cannot be unmounted and displays the error that files are being used or opened.
With this command you can easily identify which files are in use.
The most common format for this command is.
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
- List all Open Files with lsof Command
$ lsof COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME perl5.18 86 frielink1 cwd DIR 1,8 1496 171171422 /Library/PreferencePanes/Squeezebox.prefPane/Contents/server perl5.18 86 frielink1 txt REG 1,8 52864 183544244 /usr/bin/perl5.18 perl5.18 86 frielink1 txt REG 1,8 2505568 183422594 /System/Library/Perl/5.18/darwin-thread-multi-2level/CORE/libperl.dylib .... perl5.18 86 frielink1 1u REG 1,8 45133 185875296 /Users/frielink1/Library/Logs/Squeezebox/server.log </syntaxhighlight>
FD – stands for File descriptor and may seen some of the values as:
|
Also in FD column numbers like 1u:
|
TYPE – of files and it’s identification.
|
List all users files
<syntaxhighlight lang="bash">
- List all users file
$ lsof -u frielink1 COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME perl5.18 86 frielink1 cwd DIR 1,8 1496 171171422 /Library/PreferencePanes/Squeezebox.prefPane/Contents/server perl5.18 86 frielink1 txt REG 1,8 52864 183544244 /usr/bin/perl5.18 perl5.18 86 frielink1 txt REG 1,8 2505568 183422594 /System/Library/Perl/5.18/darwin-thread-multi-2level/CORE/libperl.dylib perl5.18 86 frielink1 txt REG 1,8 43792 183422795 /System/Library/Perl/5.18/darwin-thread-multi-2level/auto/Cwd/Cwd.bundle
- List Only IPv4 & IPv6 Open Files
$ lsof -i 4 COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME perl5.18 86 frielink1 9u IPv4 0xeafb4cd1924121c9 0t0 UDP *:slim-devices perl5.18 86 frielink1 10u IPv4 0xeafb4cd190abe809 0t0 TCP *:slim-devices (LISTEN) perl5.18 86 frielink1 25u IPv4 0xeafb4cd190ab9d89 0t0 TCP *:websm (LISTEN)
- List Open Files of TCP Port ranges 1-1024
$ lsof -i TCP:1-1024
- Exclude User with ‘^’ Character
$ lsof -i -u^root COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME perl5.18 86 frielink1 9u IPv4 0xeafb4cd1924121c9 0t0 UDP *:slim-devices perl5.18 86 frielink1 10u IPv4 0xeafb4cd190abe809 0t0 TCP *:slim-devices (LISTEN) perl5.18 86 frielink1 25u IPv4 0xeafb4cd190ab9d89 0t0 TCP *:websm (LISTEN) perl5.18 86 frielink1 28u IPv4 0xeafb4cd192c501c9 0t0 UDP *:61744 perl5.18 86 frielink1 29u IPv6 0xeafb4cd192c4f9d1 0t0 UDP *:* </syntaxhighlight>
Safari
Always looking for the quick-key for moving between the different open Safari-windows? what about Command-Tilde (⌘-`).
- Apple Safari Features, Learn about the 250+ innovative features available in Safari.
JavaScripts
When you are debugging JavaScript, you will find some installed javascripts from Safari. They are located in the directory:
- /Users/<your-user-name>/Library/Caches/com.apple.Safari/Extensions
Examples are:
- ../iTube Studio.safariextension/analysismodule/website_extract.js
- ../Exposer.safariextension/inject.js