Basic Modelling Concepts: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
<br>The university has faculties which exists on its departments (composition). Departments uses employees/members (aggregation). | <br>The university has faculties which exists on its departments (composition). Departments uses employees/members (aggregation). | ||
|} | |} | ||
In Java: | |||
<pre> | |||
class Circle { | |||
</pre> | |||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
Revision as of 17:26, 18 January 2015
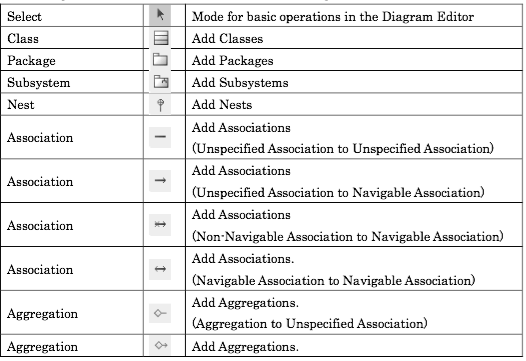
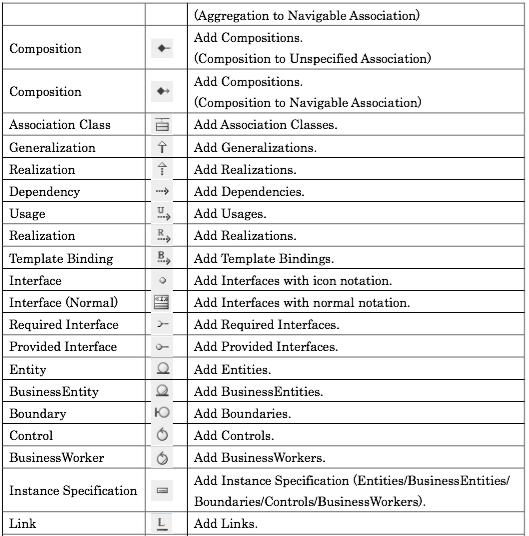
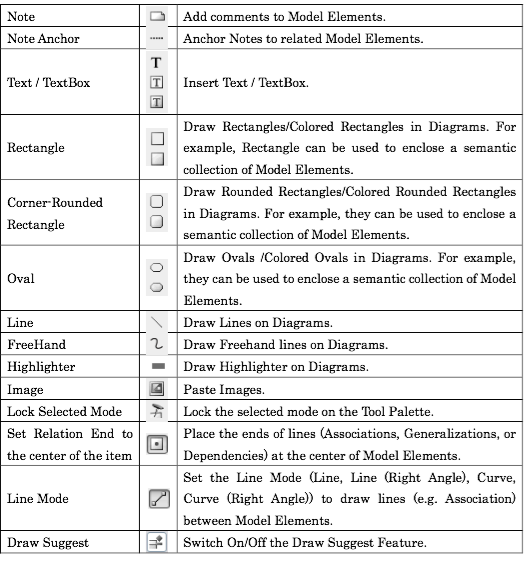
Modelling tools have their own interpretation of how diagrams, icons are used. This webpage tries to give some clues on how this implementation are made.
| Diagram Elements | Sterotypes |
|---|---|
  |
 |
Object Orientation Basic Elements
Basic OO Elements:
Association
| https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/f/f5/BidirectionalAssociation.png | https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/0/05/UnidirectionalAssociation.png |
|---|---|
| A bidirectional association | Unless otherwise specified, navigation across an association is bidirectional, although it may be limited to just one direction by adorning some end with an arrowhead pointing to the direction of traversal. |
| Description | |
| Association defines a relationship between classes of objects that allows one object instance to cause another to perform an action on its behalf. | |
Aggregation
| https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/d/d0/Aggregation-Composition3.png |
|---|
| A bidirectional association |
| Description |
| Association defines a relationship between classes of objects that allows one object instance to cause another to perform an action on its behalf. A "uses" B = Aggregation : B exists independently (conceptually) from A.
|
Composition
In Java:
class Circle {
See also
http://agilemodeling.com/images/style/classDiagramAnalysisVsDesign.gif top
- Agile Modeling, Class Diagrams Guidelines. See example above.