Data Modelling: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{TOCright}} | {{TOCright}} | ||
Data Modelling in software engineering is the process of creating a data model for an information system by applying formal data modelling techniques <ref>[[wikipedia:Data_Modeling|Wikipedia]] Data Modelling</ref>. | Data Modelling in software engineering is the process of creating a data model for an information system by applying formal data modelling techniques <ref>[[wikipedia:Data_Modeling|Wikipedia]] Data Modelling</ref>. | ||
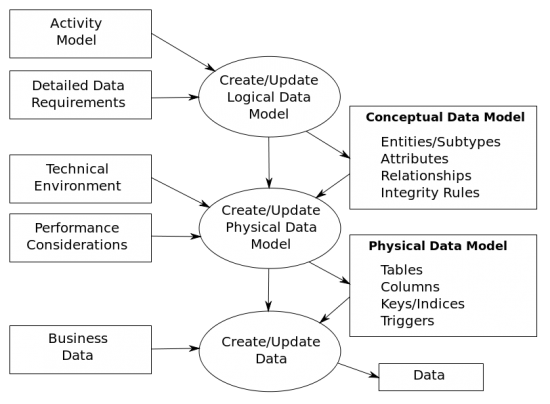
Data modeling is a process used to define and analyze data requirements needed to support the business processes within the scope of corresponding information systems in organizations. Therefore, the process of data modeling involves professional data modelers working closely with business stakeholders, as well as potential users of the information system. There are three different types of data models produced while progressing from requirements to the actual database to be used for the information system. | |||
[[image:Data_Modelling_Overview.png|thump|550px|right|Data Modelling Overview]] | [[image:Data_Modelling_Overview.png|thump|550px|right|Data Modelling Overview]] | ||
Revision as of 11:41, 14 November 2012
Data Modelling in software engineering is the process of creating a data model for an information system by applying formal data modelling techniques [1].
Data modeling is a process used to define and analyze data requirements needed to support the business processes within the scope of corresponding information systems in organizations. Therefore, the process of data modeling involves professional data modelers working closely with business stakeholders, as well as potential users of the information system. There are three different types of data models produced while progressing from requirements to the actual database to be used for the information system.